What is the mandatory employment system for the disabled?
The mandatory employment system for the disabled refers to a system in which employers who employ 50 or more full-time workers on average per month are required to hire disabled workers at a rate or higher specified by Presidential Decree within the range of 5/100 of the total number of employees. Simply put, this means that companies above a certain size are required to hire people with disabilities. Employment obligations are imposed on national organizations, local governments, and employers who employ more than 50 full-time workers per month. Additionally, the mandatory employment rate for people with disabilities in national, local governments, and public institutions in 2024 is 3.8% of the total number of employees, and in the case of private companies, it is 3.1%. Employers who hire disabled people above the mandatory employment rate will be paid incentives for the excess number of employees, and a levy will be imposed if companies with more than 100 full-time workers fail to meet their employment obligations.
What is the Employment Incentive for the Disabled?
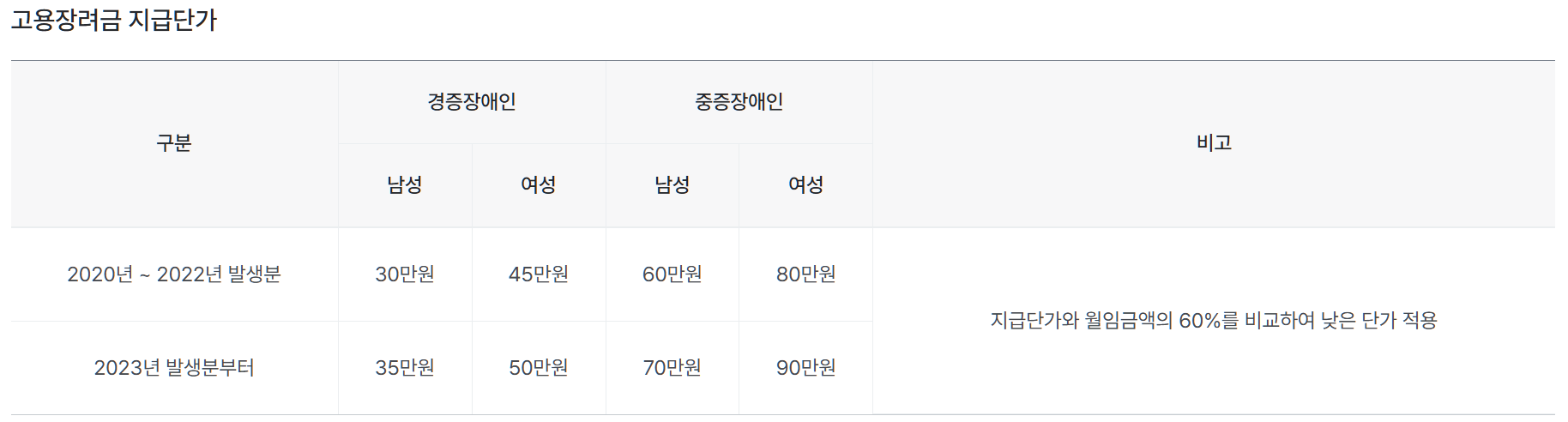
The disabled employment incentive is a system that provides a certain amount of support to employers who hire disabled people in excess of the mandatory employment rate. However, support is available only to those with disabilities who receive more than the minimum wage and those who have received approval for exemption from minimum wage. Exclusion from the application of the minimum wage means that the minimum wage is not applied to those who have significantly low work ability due to mental or physical disabilities or are otherwise deemed inappropriate to apply the minimum wage. To do this, the employer must obtain approval from the Minister of Employment and Labor. In particular, disabled workers who do not subscribe to employment insurance are excluded from the number of people eligible for employment incentives. Incentives are eligible for payment only when two or more disabled workers are employed.
Employment incentives for the disabled will continue to be paid if the monthly employment status exceeds the mandatory employment rate. The right to receive employment incentives lasts for three years. The unit price of employment incentives varies depending on the degree of disability and gender of the disabled person employed. For employees who meet and exceed the mandatory employment rate in order of employment date, the lower amount of the payment unit price or 60% of the monthly wage is paid to the employer. As of the first quarter of 2024, employment incentives for the disabled were paid to 5,445 businesses, and the payment amount was approximately KRW 116.1 billion.
The Employment Incentive for the Disabled cannot be paid in conjunction with the New Employment Incentive for the Disabled. The New Employment Incentive for the Disabled is an incentive paid to employers who have between 5 and 50 employees and keep newly hired disabled people employed for more than 6 months. Up to 1 year and up to 2 people can apply.
What is the disabled employment levy?
The disabled employment charge is a public fee that must be paid by employers who have an obligation to hire disabled people if they hire disabled people who fall below the mandatory employment rate. Employers who employ 50 or more full-time workers are required to hire disabled workers according to the statutory mandatory employment rate, and employers who employ 100 or more full-time workers are required to report and pay a fee if mandatory employment is not implemented. This applies to business owners with more than 100 full-time workers on average per month, not in a specific month. Private employers, heads of state agencies and local governments, superintendents of education, and heads of public institutions and local public enterprises are all subject to reporting. The reporting deadline is 1.1 every year. ~ January 31 and must be paid by January 31. If the report is filed after the reporting deadline or payment is made after the payment deadline, an additional fee or late payment fee will be charged. If the contribution is more than 1 million won, it is possible to pay in four equal installments.
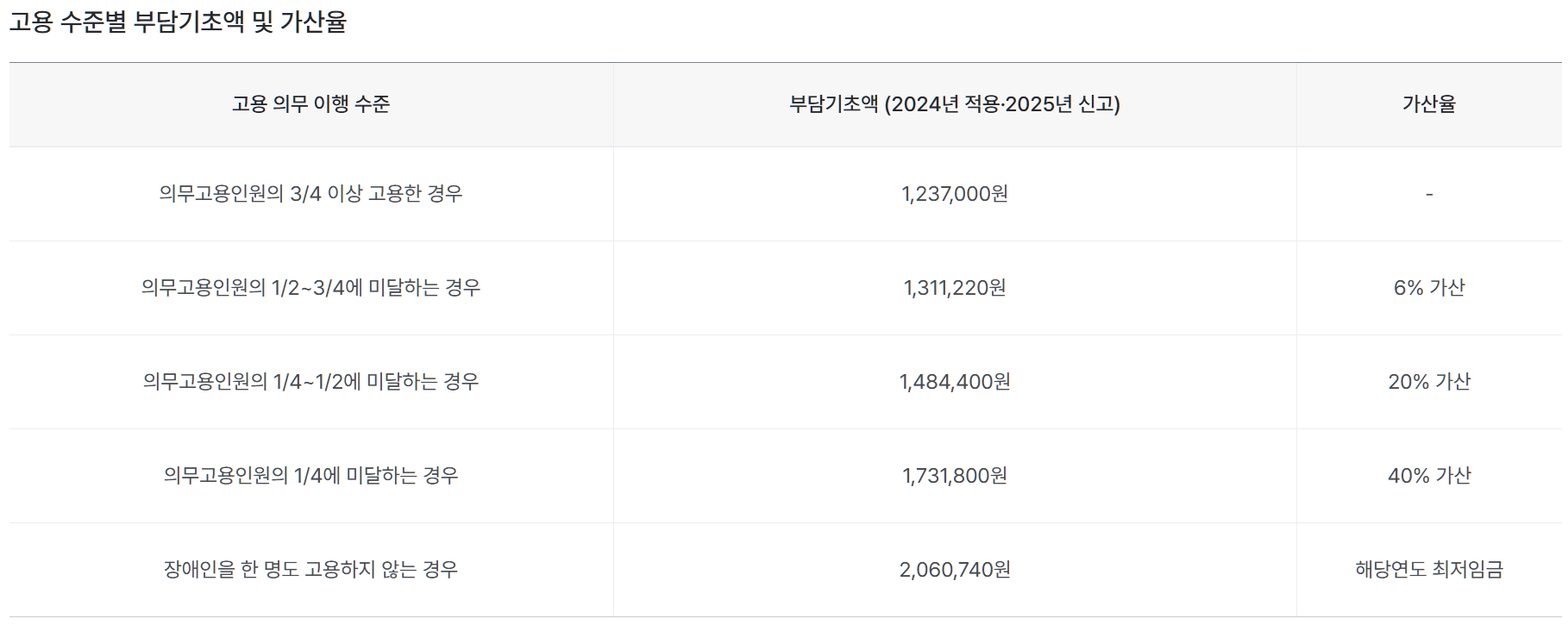
The payment amount is calculated by subtracting the number of full-time disabled workers employed from the number of disabled workers to be employed and multiplying by the basic burden amount according to the employment level, and the total amount is paid annually. The basic burden is determined by adding 1/4, 1/2, and 3/4 of the number of mandatory employees. If no disabled people are employed, the basic burden is 2,060,740 won, applied in 2024 (reported in 2025). no see. As of the first quarter of 2024, there are 8,536 businesses that have collected employment fees for the disabled, and the amount collected is approximately KRW 821 billion.
Disabled Persons as Workers
The employment incentives for the disabled promote the stability of the work life of disabled workers and encourage employment, and the cost of hiring the disabled by equalizing the economic burden of employers who hire and do not employ disabled people, reflecting the ideology of social solidarity and responsibility. We learned about the employment levy for the disabled to compensate for this. Both systems are systems that help disabled people move forward as workers and enable employers to contribute to society. We hope that it will be utilized well and help disabled workers and business owners.

Reference:
Employment incentive support, Korea Employment Agency for the Disabled
Disabled Employment Levy, Korea Employment Agency for the Disabled
Mandatory employment system for the disabled, Korea Employment Agency for the Disabled